Using Ohm's Law Describe How These Physical Quantities
What is the amount of current I in this circuit. The formula of Ohms law is as follows voltage Voltage V is equal to current Current I multiplied by resistance Resistance R.

For The Graph Shown In The Figure What Physical Quantity Does The Slope Of The Graph Represent For Ohmic Material The Plot Shows The Potential As A Function Of Current The Current
V IR P VI are the basic quantities which relate them.

. The current flowing through the resistor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it. There are many electrical appliances like electric heater kettle operates based on the principle of. A simple circuit has a single voltage source and a single resistor.
In this first example we will calculate the amount of current I in a circuit given values of voltage E and resistance R. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Ohm law Units of Quantities used in Ohms Law Ohms law relates four basic electrical quantities.
E I x R. It helps to calculate the power efficiency current voltage and resistance of an element of an electrical circuit. Write the equation for Ohms law.
Ohms Law summarizes these facts in a simple easy-to-use equation. In this first example we will calculate the amount of current I in a circuit given values of voltage E and resistance R. R V I Resistance Voltage Current.
Ohms Law is a formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage current and resistance in an electrical circuit. For calculation and simplifying of electric circuits measuring of Current Voltage and Resistance we can use Ohms Law in the following three forms 1. If we know the values of any two of the three quantities voltage current and resistance in this circuit we can use Ohms Law to determine the third.
Ohm performed repeated experiments on a resistor applied different voltages measured current and found relationship between these quantities. Rubber balloon Glass Plastic Air Wood. Lets understand their units.
Often referred to as the Ohms law equation this equation is a powerful predictor of the relationship between potential difference current and resistance. Finally taking the measured figures for resistance and current use the Ohms Law equation to calculate circuit voltage. It is equal to 1 voltampere.
The SI unit of resistance is ohms and is denoted by Ω. Through the rest of this unit of The Physics Classroom this equation will become the most common equation which we see. There are different applications of ohms law.
If we know the values of any two of the three quantities voltage current and resistance in this circuit we can use Ohms Law to determine the third. What are these examples of. Because the graph shows current as a function of voltage we have to rearrange Ohms law in that form.
To students of electronics Ohms Law E IR is as fundamentally important as Einsteins Relativity equation E mc² is to physicists. Voltage is V and is measured in Volts The current flowing through the conductor is I and it represented in amperes the resistance is R and is measured in ohms. This law is used to determine the different electrical quantities such as current voltage resistance power conductance etc.
05 Using Ohms law describe how these physical quantities of these circuit elamante would ralate to each nther b. Ohms Law as a Predictor of Current. In Ohms law V I R V I R the constant of proportionality is the resistance R.
Describe the relationship between voltage current and resistance using Ohms law. This shows that the slope of the line of I versus V is 1 R 1 R. Voltage Current Resistance 3 V IR The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm Ω.
If the resistance is not constant the previous equation cannot be called Ohms law but. The unit for resistance is an ohm and is given the symbol Ω upper case Greek omega. The plot shows that current is proportional to voltage which is Ohms law.
VI x R In Ohms law equation if two of the physical quantities are known the third physical quantity can be obtained by calculation. Voltage is proportional to Current. Ohms Law Is The Relationship Between Voltage Current and Resistance.
V I x R Voltage Current x Resistance Volt Amps x Ohms Ω 2. Ohms law formula potential difference formula is made use of to calculate the Resistance Current and Voltage in any given circuit if any of the. These are the standard measurement units for electrical currents voltage and resistance.
I V R 1 R V I V R 1 R V. This law is one of the most basic laws of electricity. He finally published the law in 1827 and generalized his observations in single statement.
I V R Current Voltage Resistance Amps Volts Ohms Ω 3. Where I is the current through the conductor in units of amperes V is the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts and R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms. The statement P VI is actually Joules law.
Figure 1 shows the schematic for a simple circuit. Copper Penny Aluminum Cans Gold Silver. Compare this calculated figure with the measured figure for circuit resistance.
1Ω 1V A 1 Ω 1 V A. What are these examples of. 05 Is any physical quantity among current potential difference and resistance the same for all these circuit elements.
Formula of Ohms Law. Rearranging I VR gives R VI and so the units of resistance are 1 ohm 1 volt per ampere. More specifically Ohms law states that the R in this relation is constant independent of the current.
Consider all circuit elements except for the battery and answer the following questions. Voltage Current Resistance V IR V voltage I current and R resistance. Ohms law formula is articulated as.
Explain how you can find any one of. Taking the measured figures for voltage and current use the Ohms Law equation to calculate circuit resistance. You need to be able to describe the quantities as measurements much the same as temperature mass length volume or any other types of physical quantities.
Start studying Physical Science Quiz. Ohms LawWatts Law and Quiz From Monday. All these quantities are linked together in Ohms law formulas.
What is the amount of current I in this circuit. Alternate statements of Ohms law are that the current I in a conductor equals the potential difference V across the conductor divided by the resistance of the conductor or simply I V R and that the potential difference across a conductor equals the product of the current in the conductor and its resistance V IR.

Ohm S Law Definition Formula Applications Of Ohm S Law Videos

State Ohms Law Write The Necessary Conditions For Its Validity How Is This Law Verified Experimentally What Will Be The Nature Of Graph Between Potential Difference And Current For A Conductor Name

Ohm S Law Of Current Electricity Definition Limitations Videos Examples

Electrical Quantities And Units Coloring Notes Teacher Resources Physical Science Physics

State Ohms Law Write The Necessary Conditions For Its Validity How Is This Law Verified Experimentally What Will Be The Nature Of Graph Between Potential Difference And Current For A Conductor Name

What Are The Four Laws Of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Book Writing Tips Physics Concepts

Lesson Plan Of Physical Quantities And System International Units Measurements Of Physical Quantities General Science Gr Physics Lessons Physics Basic Physics

Ohm S Law Electrical Resistance Chart Manufacturer Supplier Exporter From New Delhi In 2020 Ohms Law Educational Maps Electricity

V I Graph For A Conductor Is As Shown In The Figure Curren Scholr

Ohm S Law Problems Physics Ohms Law Physics Conceptual Physics
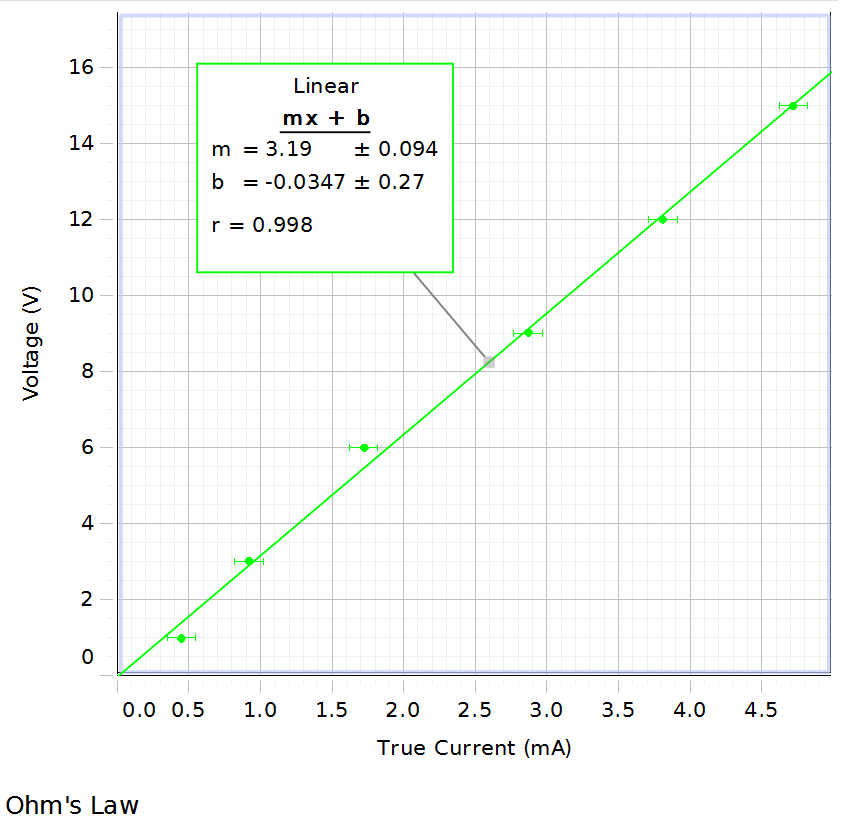
Solved Ohm S Law Lab 1 What Was Your Value For The Slope Chegg Com

Physical Quantities Posters Physics Formulas Physics Math Methods

Ohm S Law Doodle Sheets Visual Guided Notes Physics Ohms Law Guided Notes Physics High School
Unified Lecture 3 Measurement Of Physical Quantities Units
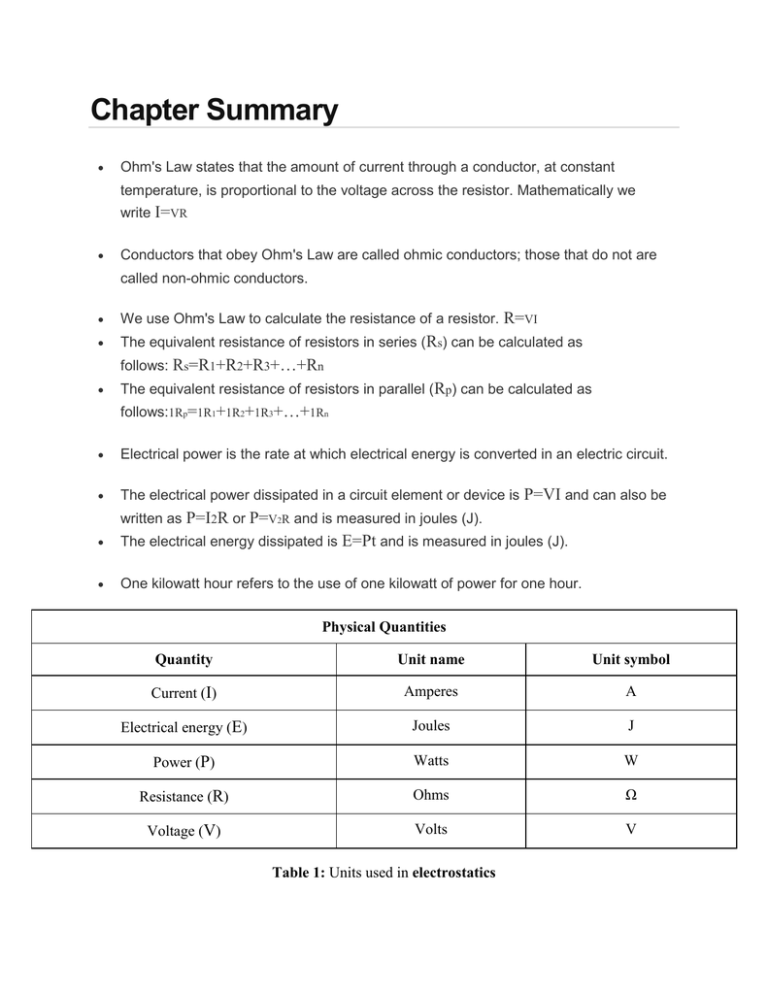
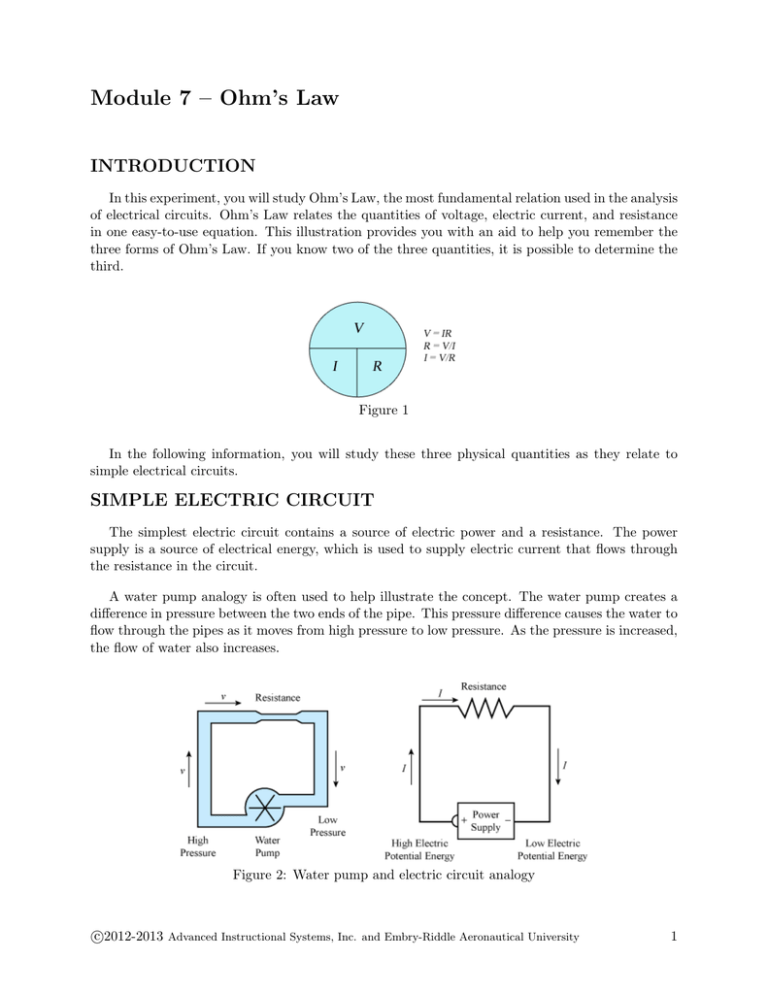


Comments
Post a Comment